What Causes Hair Loss: 10 Major Reasons with Treatments
What causes hair loss? Hair loss can affect just your scalp or your entire body. It can be the result of heredity, hormonal changes, medical conditions or medications. Anyone can experience hair loss, but it’s more common in men.
Baldness typically refers to excessive hair loss from your scalp. Hereditary hair loss with age is the most common cause of baldness. Some people prefer to let their hair loss run its course untreated and unhidden. Others may cover it up with hairstyles, makeup, hats or scarves. And still, others choose one of the treatments available to prevent further hair loss and to restore growth.
Symptoms of hair loss
Hair loss can appear in many different ways, depending on what’s causing it. It can come on suddenly or gradually and affect just your scalp or your whole body. Some types of hair loss are temporary, and others are permanent.
Signs and symptoms of hair loss may include:
- Gradual thinning on top of the head. This is the most common type of hair loss, affecting both men and women as they age. In men, hair often begins to recede from the forehead in a line that resembles the letter M. Women typically retain the hairline on the forehead but have a broadening of the part in their hair.
- Circular or patchy bald spots. Some people experience smooth, coin-sized bald spots. This type of hair loss usually affects just the scalp, but it sometimes also occurs in beards or eyebrows. In some cases, your skin may become itchy or painful before the hair falls out.
- Sudden loosening of hair. A physical or emotional shock can cause hair to loosen. Handfuls of hair may come out when combing or washing your hair or even after gentle tugging. This type of hair loss usually causes overall hair thinning and not bald patches.
- Full-body hair loss. Some conditions and medical treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer, can result in the loss of hair all over your body. The hair usually grows back.
- Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp. This is a sign of ringworm. It may be accompanied by broken hair, redness, swelling and, at times, oozing.
Several factors can increase your risk of hair loss, including:
- Family history of balding, in either of your parent’s families
- Age
- Significant weight loss
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and lupus
- Stress
Preventions for hair loss
Most baldness is caused by genetics (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness). This type of hair loss is not preventable.
These tips may help you avoid preventable types of hair loss:
- Avoid tight hairstyles, such as braids, buns or ponytails.
- Avoid compulsively twisting, rubbing or pulling your hair.
- Treat your hair gently when washing and brushing. A wide-toothed comb may help prevent pulling out hair.
- Avoid harsh treatments such as hot rollers, curling irons, hot oil treatments, and permanents.
- Avoid medications and supplements that could cause hair loss.
- Protect your hair from sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet light.
- Stop smoking. Some studies show an association between smoking and baldness in men.
- If you are being treated with chemotherapy, ask your doctor about a cooling cap. This cap can reduce your risk of losing hair during chemotherapy.

Treatment for hair loss
-
Medication
Medications will likely be the first course of treatment for hair loss. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications generally consist of topical creams and gels that you apply directly to the scalp. The most common products contain an ingredient called minoxidil (Rogaine).
Doctor may recommend minoxidil in conjunction with other hair loss treatments. Side effects of minoxidil include scalp irritation and hair growth in adjacent areas, such as your forehead or face.
Prescription medications may also treat hair loss. Doctors prescribe the oral medication finasteride (Propecia) for male-pattern baldness. You take this medication daily to slow hair loss. Some men experience new hair growth when taking finasteride.
Rare side effects of finasteride include diminished sex drive and impaired sexual function. There may be a link between the use of finasteride and a more serious type (high-grade) of prostate cancer.
Medical Procedures
Sometimes, medications aren’t enough to stop hair loss. There are surgical procedures to treat baldness.
-
Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery involves moving small plugs of skin, each with a few hairs, to bald parts of your scalp. This works well for people with inherited baldness since they typically lose hair on the top of the head. Because this type of hair loss is progressive, you would need multiple surgeries over time.
-
Scalp Reduction
In a scalp reduction, a surgeon removes part of your scalp that lacks hair. The surgeon then closes the area with a piece of your scalp that has hair. Another option is a flap, in which your surgeon folds scalp that has hair over a bald patch. This is a type of scalp reduction.
Tissue expansion can also cover bald spots. It requires two surgeries. In the first surgery, a surgeon places a tissue expander under a part of your scalp that has hair and is next to the bald spot. After several weeks, the expander stretches out the part of your scalp that has hair.
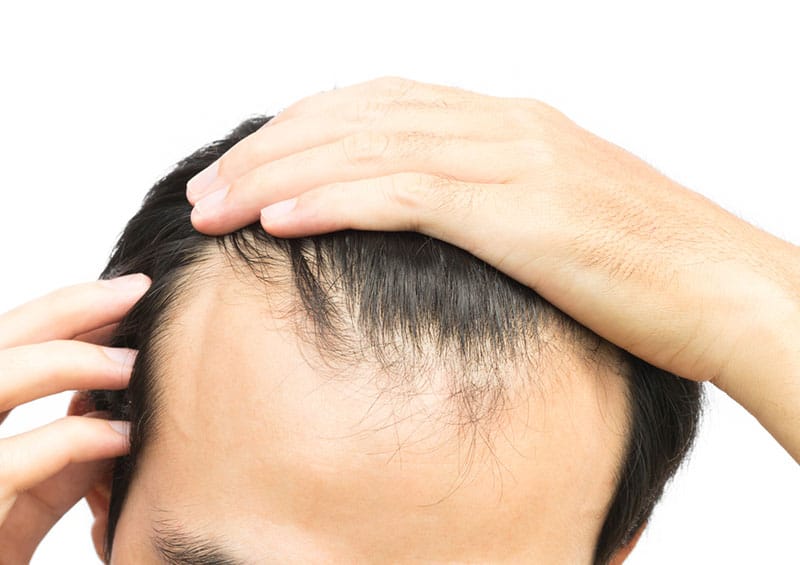
Causes of hair loss in men and women
Possible causes of hair loss include:
-
Androgenetic alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is another term for male or female pattern baldness. It is a very common cause of hair loss. Both male and female pattern baldness is genetic. Males tend to lose hair from the temples and crown of the head. In females, hair usually becomes thinner all over the head.
Androgenetic alopecia is more likely to happen as a person ages but can start at any point after puberty. Many females who experience androgenetic alopecia develop it after going through the menopause. This means that hormones may have something to do with it.
-
Pregnancy
Some women may experience excessive hair loss shortly after giving birth. This is due to a decrease in estrogen levels. This type of hair loss is a temporary condition and usually resolves within a year or sooner.
To help hair return to its normal condition, try:
- using a volumizing shampoo and conditioner
- using products designed for fine hair
- avoiding intensive conditioners or conditioning shampoos as these can be too heavy for fine hair
- applying conditioner to the ends of the hair, rather than the scalp, to avoid weighing hair down
-
Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a condition where the hair remains in the telogen (natural shedding) phase of the growth cycle. This causes more hair to fall out, sometimes in handfuls. Telogen effluvium is usually a temporary condition that resolves over time. It is advisable to see a doctor find out the cause.
-
Anagen effluvium
Anagen effluvium causes large amounts of hair to fall out rapidly during the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle. The condition may cause hair to fall out from the head, as well as from other parts of the body, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
Causes of anagen effluvium include:
- chemotherapy
- radiation
- fungal infections
- autoimmune disease
Treatment for this condition depends on the cause but can include a topical solution of minoxidil.
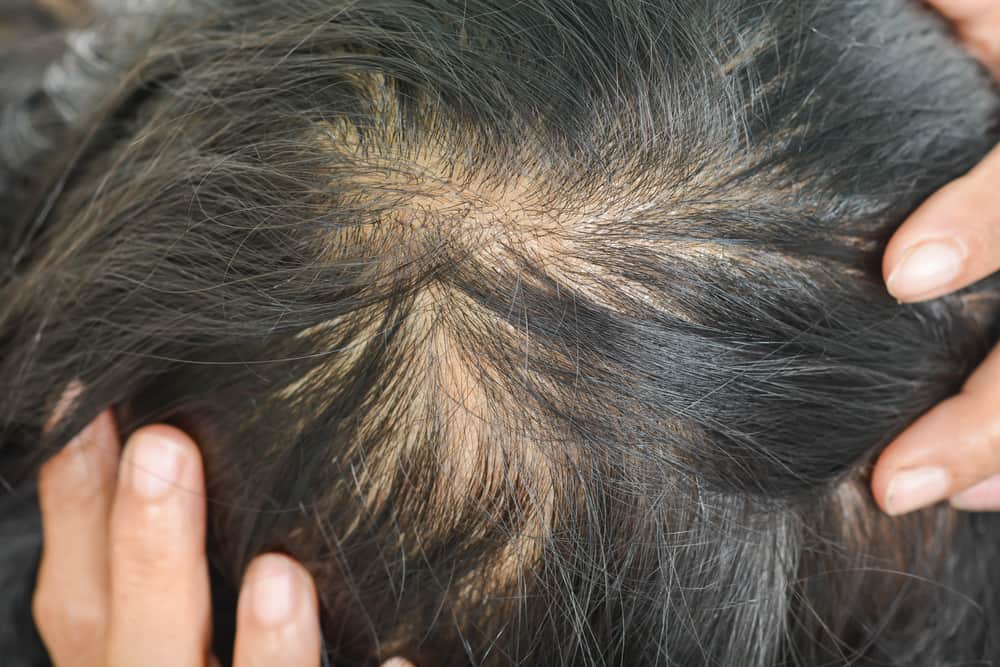
-
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes hair to fall out suddenly. The immune system attacks hair follicles, along with other healthy parts of the body.
Hair from the scalp, as well as eyebrows and eyelashes, may fall out in small chunks.
If a person has this condition, they should see a doctor. A doctor may prescribe medication to help the hair grow back.
-
Traction alopecia
Traction alopecia is hair loss due to pulling hair into tight hairstyles, which causes it to break and come loose. Hairstyles associated with this condition include:
- tight buns or ponytails
- braids
- cornrows
- extensions
If traction alopecia continues, a person may develop bald spots and thin of the hair.
-
Medications
Certain medications have side effects that can cause hair to fall out.
Examples of such medications include:
- blood thinners, such as warfarin
- Accutane, to treat acne
- antidepressants, including Prozac and Zoloft
- beta-blockers
- cholesterol-lowering drugs, such as Lopid
If a person thinks hair loss may be due to a medication they are taking, they should consider seeing a doctor for an assessment. The doctor might be able to reduce the dosage or switch the person to a different medication.
-
Nutritional deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can cause hair to fall out. Extreme diets that are too low in protein and certain vitamins, such as iron, can sometimes cause excessive hair shedding.
A person should see a doctor for a blood test to check if they have a nutritional deficiency that could be causing their hair to fall out.
-
Birth control pills
People may experience hair loss while using birth control pills. Others might experience hair loss several weeks or months after they stop taking them.
If people are taking birth control pills, they can choose one that has a low androgen index. This may help to lower the risk of hair loss.
Examples of birth control pills with a lower androgen index include:
- Desogen
- Ortho-Cept
- Ortho-Cyclen
Orval and Lonstein have a higher androgen index.
-
Ringworm
Ringworm is a fungal infection that can cause hair loss. Ringworm on the scalp, or tinea capitis, can cause temporary bald areas on the head.
Symptoms include:
- a small spot that gets bigger, causing scaly, bald patches of skin
- brittle hair that breaks easily
- itchy, red patches of skin in the affected areas
- oozing blisters on the scalp
- ring-like patches, with a red outside and the inside of the circle matching the skin tone
If ringworm does not heal by itself, then a doctor may prescribe an antifungal medicine.