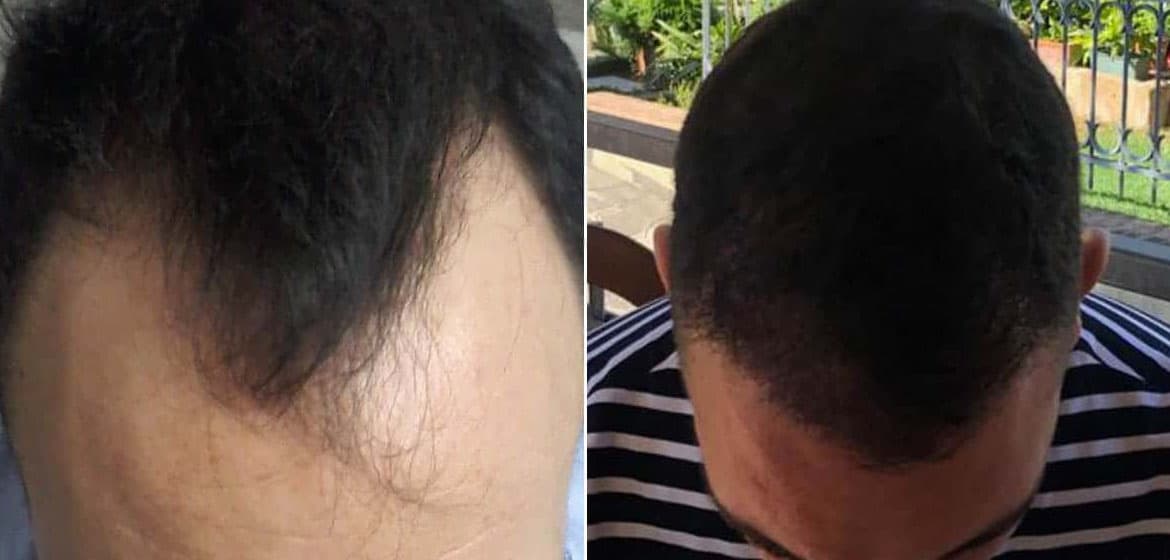
Before and after hair transplant: Step-by-Step Situation
Hair loss is distressing, but hair transplantation restores hair and boosts confidence. Before and after hair transplant can impact well-being with the right approach.
While not a permanent solution, it can boost hair thickness and confidence for many. This article covers hair transplantation, recovery, key considerations, and post-procedure expectations.
Hair transplantation transfers healthy hair follicles to bald areas using microsurgery techniques. Hair transplant surgery is a viable option for hair thinning or loss. In hair transplantation, we add the patient’s own healthy hair to the spilt area.
Each individual receives a personalized hair transplantation procedure. The doctor collects hair follicles from the patient’s head, focusing on the back.
During the hair transplant procedure, they are relocated to areas with minimal or no hair. The goal of this method is to give hair the most natural and healthy appearance possible.
The most common type of hair loss we encounter today is male pattern hair loss.
Common symptoms: receding hairline in forehead and visible apex. Male pattern spillage is also a similar thing in women.
Today, about half of all men over the age of 50 struggle with hair loss.
Explore the amazing changes seen in the gallery featuring hair plugs before and after photos.
Things to consider before Hair Transplant
Hair transplants generally have a higher success rate than over-the-counter hair restoration solutions. But there are several factors to take into account:
- Around 10-80% of transplanted hair is likely to regrow in 3-4 months.
- Like natural hair, the transplanted hair will also thin over time.
- People with inactive hair follicles may have less successful hair transplants. Plasma therapy may help regrow 75% or more of transplanted hair.
Hair transplants are not suitable for everyone. They are mainly used to add hair in cases of balding or thinning, or hair loss from an injury.
Transplants are performed using your existing hair. They are not effective for individuals with:
- extensive hair thinning and balding
- hair shedding as a result of chemotherapy or other drugs
- dense scars on the scalp from wounds
Expectations
After the surgery, your scalp may be very tender. You may need to take pain medications for several days.
Your surgeon will have you wear bandages over your scalp for at least a day or two. He may also prescribe an antibiotic or an anti-inflammatory drug for you to take for several days. Most people can return to work 2 to 5 days after the operation.
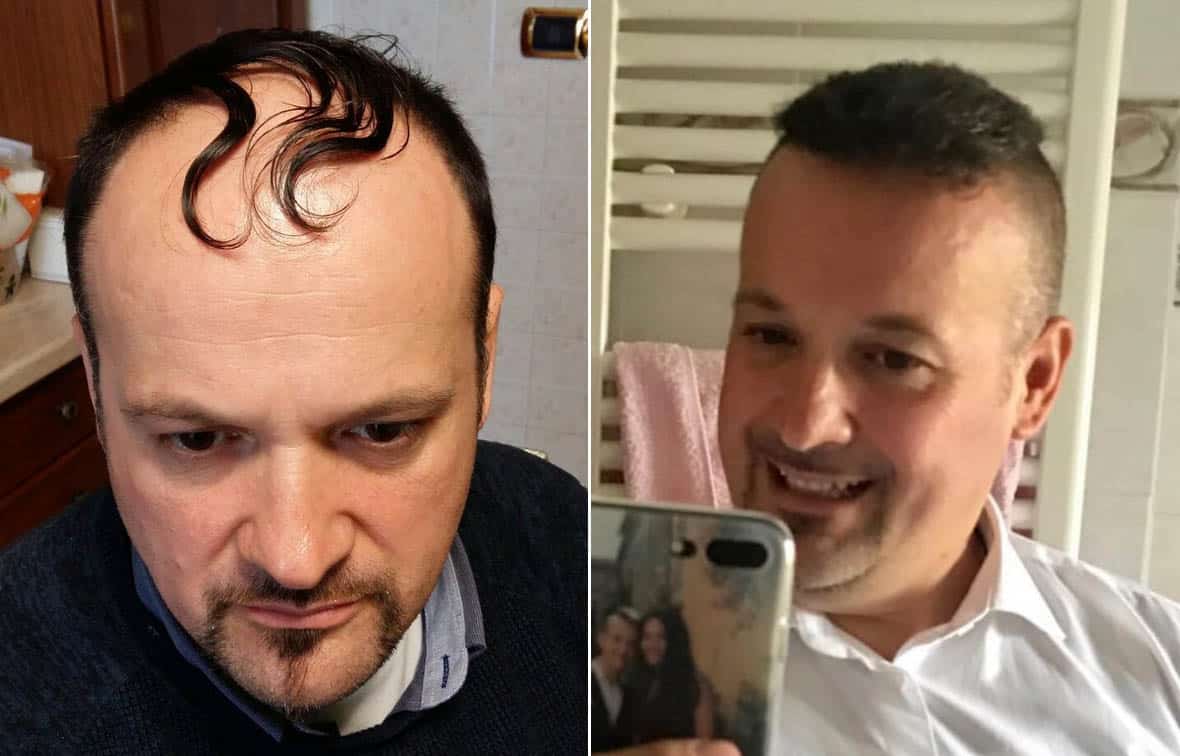

How does hair transplant work
In simple terms, a hair transplant involves moving hair from a place where you have it to a place where you don’t. Usually, it comes from the back of your head, but it can also come from different parts of your body.
The surgeon will anesthetize and clean the area before the hair transplant. If you wish, you can also opt for sedation to remain unconscious during the procedure.
Your surgeon will then carry out one of two transplant techniques: FUT or FUE.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT is also referred to as follicular unit strip surgery (FUSS). Here are the steps your surgeon will follow to perform a FUT procedure:
- The doctor removes a part of your scalp using a surgical knife, usually from the back of your head. The strip’s dimensions are usually around 6 to 10 inches in length and can extend from one ear to the other.
- The surgical area from where the scalp was excised is then sealed with sutures.
- The surgeon and their team dissect the scalp strip into tinier sections using a scalpel. They might divide the strip into up to 2,000 smaller units, known as grafts hair. Some of these grafts may only have a single hair.
- The doctor makes small cuts on your scalp to insert the hair, using a needle or blade.
- The surgeon then implants hairs from the excised scalp segment into the incisions. This procedure is referred to as grafting.
- Finally, the surgical areas are covered with bandages or gauze.
The exact number of grafts you get is determined by the:
- nature of your hair
- dimensions of the transplant area
- hair quality (including its density)
- color of your hair
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- After shaving the back of the head, individual hairs are extracted one by one (grafts)
- Hair grafts are inserted into small wounds in the scalp.
- You’ll have a lot of tiny scars, but they won’t be noticeable.
Hair transplants take one day. But, if a large area is being treated, many treatments may be necessary. These treatments are usually spaced a few months apart.
Your surgeon will instruct you on how to care for your transplant. To help recovery and hair restoration, you should be provided with a spray to apply.
FUE Hair Transplant Procedure
Micromotors accelerate FUE, extracting hair from the neck, breasts, and back for transplantation.
Small, thin incisions mimic natural hair growth angles for personalized hairline patterns.
Donor area trimmed and numbed, 1mm grafts implanted into thinning areas via channels.
Skilled team and time needed for thick hair transplant. Requires wider channels and denser graft placement for up to 4000 grafts.
In recent years, FUE hair transplant has overtaken the FUT technique.
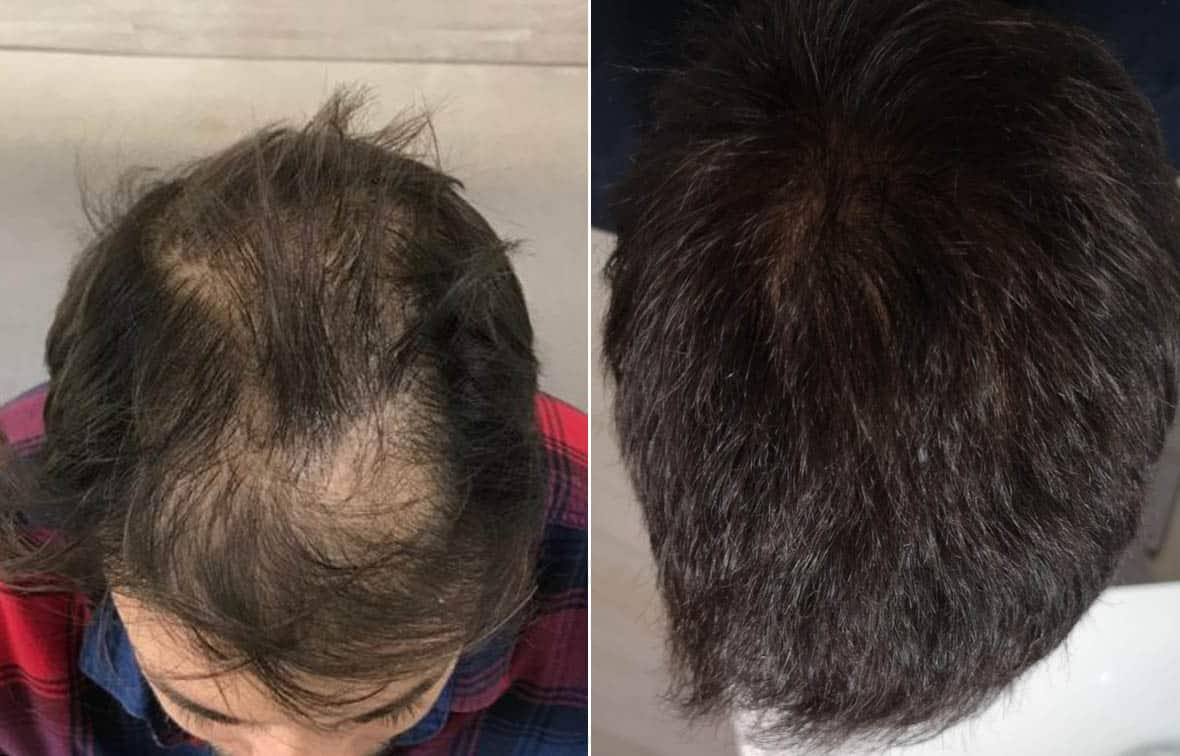
Reconstructing The Frontal Hairline
The frontal hairline is often the most plain part of a completed hair transplant. But, hairline requirements vary from patient to patient.
Some individuals want a hairline that is rather low and dense. A person in their 30s with a little hair loss may want to lower their hairline and fill in their temples.
Hair loss can worsen in one’s 40s, necessitating more type of hair transplant procedures. Young patients should be aware that their hair loss may persist. As a result, they may need more procedures in the future.
Hair Restoration Procedure
Hair transplantation is a one-year process that includes both before and after hair transplant. Post hair transplant, expect redness, scabbing, scab shedding, and shock hair shedding. These are typical processes. It takes a year for all the transplanted hair to grow and for the treatment’s success to be noticeable.
Redness and Crusting:
Hair transplant moves grafts from one area to another, causing redness on the skin. Crusting happens during the healing phase of this location after the operation. The formed crusts can come off in the next fifteen days.
Shock Shedding Process:
Transplanted hair sheds as remaining pieces fall off, allowing new hair to grow. It happens one to three months after the crusts have shed. The transplanted hair follicles are not damaged during the shock shedding period.
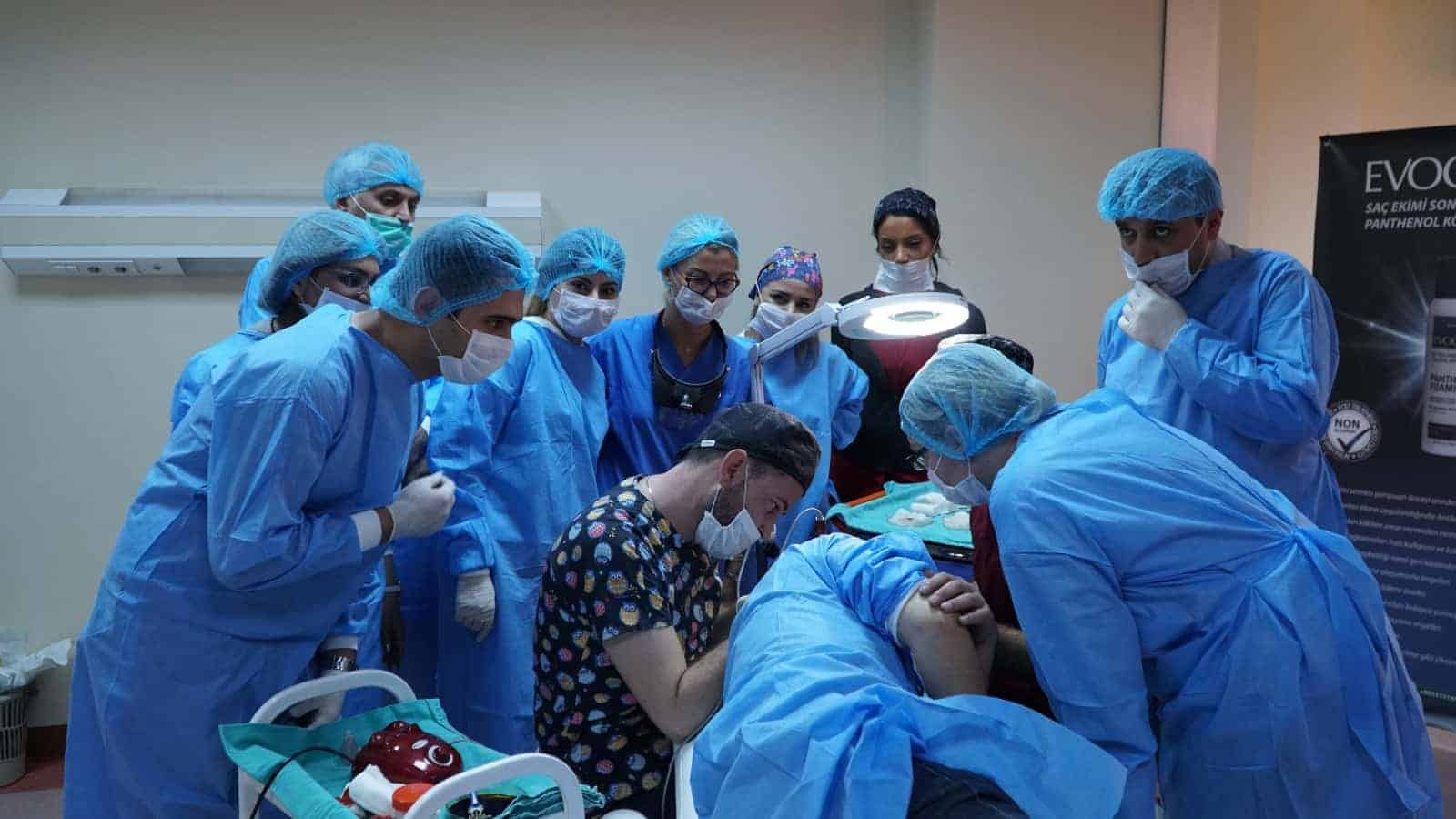
What To Expect: Hair Transplant Post-op Timeline
A hair transplant is a sensitive procedure. Following post-op guidelines is crucial for optimal hair transplant results in photos.
Most patients see benefits six to nine months following surgery. It might consumed to a year for some people. Hair transplanted will shed within 2-8 weeks after the procedure.
Post-Hair Transplant Healing Process
FUT and FUE surgeries can vary in duration, ranging from hours to days, based on the extent of the procedure. You will be released on the day of the procedure itself.
After the operation, your surgeon will remove any dressings. Your surgeon may give you an injection of triamcinolone to manage any swelling in the area.
Hair regrowth expected in a few months after surgery, but transplanted hair will shed in 2-3 weeks. Most people will see 60% of new hair growth after 6 to 9 months. Minoxidil (Rogaine) is recommended post-transplant for hair growth, but its effectiveness is uncertain.
Pain or discomfort is common at the transplant site and where hair was taken from. Your surgeon may prescribe medication for the next few days:
- pain medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil)
- antibiotics to prevent infections
- anti-inflammatories, such as an oral steroid, to relieve swelling
- Medications like finasteride (Propecia) or minoxidil (Rogaine) promote hair growth.
Here are some aftercare tips for hair transplant surgery:
- Wait for a few days after the surgery before washing your hair. Use only mild shampoos during the first few weeks.
- You can resume your normal activities, including work, after approximately 3 days.
- Avoid pressing a brush or comb down over the new grafts for at least 3 weeks.
- Wait for doctor’s approval before wearing hats or pullover shirts/jackets.
- Give yourself a break from exercising for about a week.
It’s normal for some hair to fall out during the process, so don’t worry. It may take a few months for the transplanted hair to grow and blend with the existing hair.

Tips on post-surgical FUE hair transplant
Consult an experienced doctor and check for successful FUE hair transplant. Proper post-surgery care and treatment are important for improving effectiveness.
Day 1: Do not touch and wash the surgical area the first night. If possible, cover the head with a hat while going out. On sleeping time, do elevate your head to avoid rubbing off or detaching any of the grafts. 3 or 4 pillows are helpful to achieve an ideal angle.
Day 2 – Day 4: To protect your transplant, avoid touching, scratching, or exposing it to sunlight.
Day 5 – Day 7: To help scabs soften, it is advised to shampoo the surgical area for a longer period of time. Additionally, you may resume all physical activities and sports during this time.
Week 2 – Week 4: During this time, hair follicles are in the resting phase, causing temporary hair shaft loss. Do not panic. Just continue to wash and even dye your hair as you normally do.
From Month 2 to Month 3: Follow doctor’s instructions to prevent shock loss, which may include finasteride or minoxidil.
In Month 4 until Month 6: Do remember to use a strong sunblock SPF 30 while going outside in the sun.
After Month 6 to Month 12: You can style the transplanted hair as it grows thicker and longer from fine baby hair.
Month 12 to Month 18: Congratulations to you the final hair stage and you make a change in your life, Enjoy your new hair.
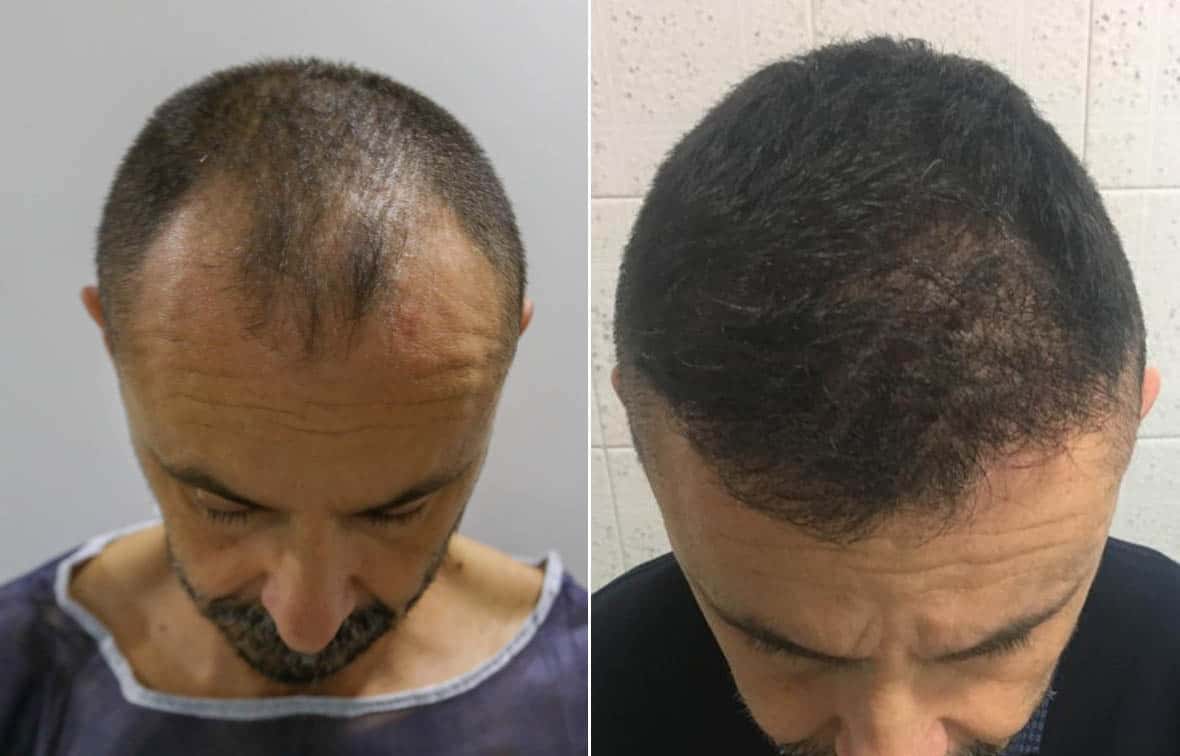
Hair transplant side effects
Scarring is a prevalent side effect that is commonly observed. Unfortunately, no procedure has been found to cure it.
More possible adverse effects are:
- infections
- crust or pus drainage around the surgical sites
- scalp pain, itching, and swelling
- inflammation of hair follicles
- bleeding
- losing sensation around the surgical sites
- visible areas of hair that don’t match the surrounding hair or are thinner
- continuing to lose hair if your hair is still balding
Minoxidil and Propecia may cause certain side effects, including:
- irritated scalp
- dizziness
- chest pain
- headaches
- irregular heart rate
- hand, foot, or breast swelling
- sexual dysfunction
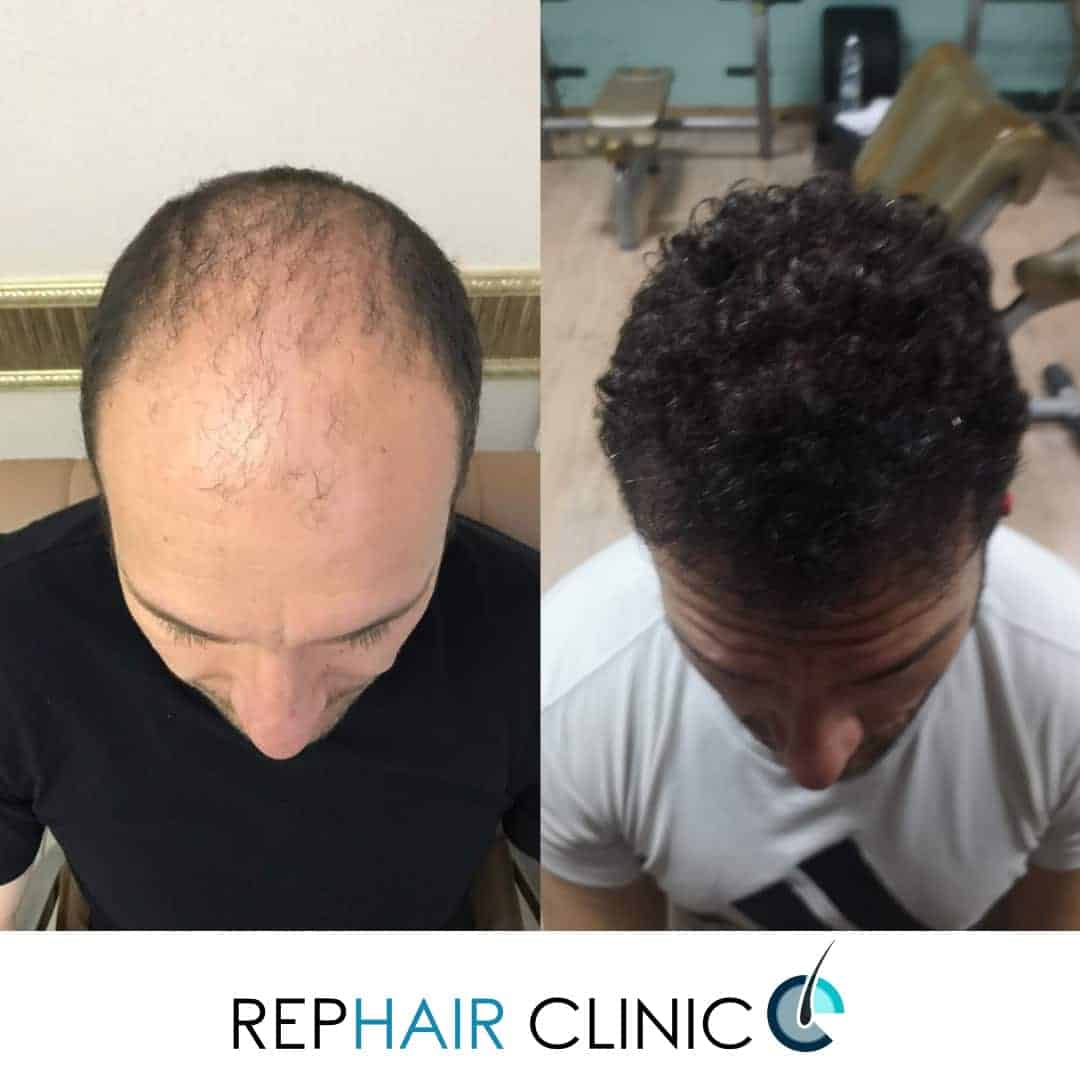
Does Hair Transplant Help to Recover Hair Loss?
Hair loss can affect either your scalp or your entire body, and it can be temporary or permanent.
Hair loss can result from genetics, hormones, health issues, or aging. While both men and women can experience hair loss, it is more common in males.
Hair transplant increases amount of hair in areas of scalp with hair loss or thinning. Thinning or balding areas can be treated by hair transplantation.
It is normal to have hair loss following a hair transplant. After a hair transplant, temporary hair loss is common. This is a short-term adverse effect of the hair restoration procedures.
It is usual for transplanted hair to fall out from shock two to eight weeks following surgery. By the third month after the transplant, the hair seems thinner.
Once the initial shock wears off, the transplanted follicles continue to create hair. Your hair will seem thicker and healthier as your transplanted hair grows. A hair transplant is a great solution for many types of hair loss problems.
What Causes Hair Thinning?
Hair loss or thinning hair happens for a variety of causes, many of which are beyond your control. Hair loss is often caused by genetic factors. Women and men have distinct types of hair loss.
Hair transplantation uses tissues from the back of men’s necks as donor hair. Achieve the desired look by moving hair follicles and restoring your hair. This procedure is straightforward and easy.
The region to be transplanted does not have to be hair-free in thin hair. Tightening is another method of hair transplanting. Hair transplantation accomplished by combining them. In other words, it is possible to transplant hair that seems thinner more.
Hair transplants boost self-esteem and happiness, especially in awkward or uncomfortable situations. As a result of sparse hair transplantation, the individual’s quality of life improves.
Hair loss or thinning can be effectively treated with hair transplants. Hair transplant success depends on the surgeon’s expertise, donor hair density, and knowledge.
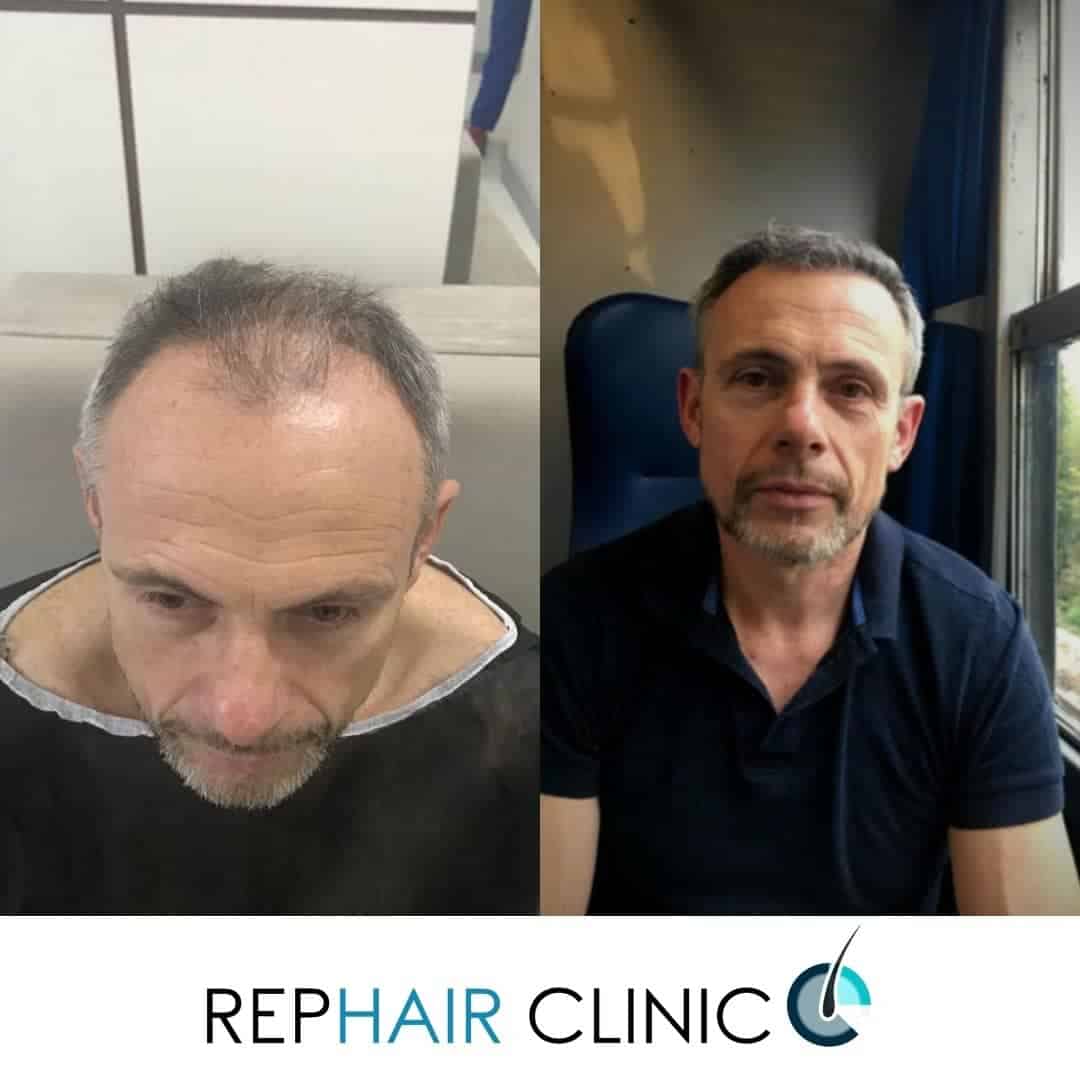
What happens after the surgery?
We wash your hair at the clinic in three days after the thinning hair transplantation. After surgery, the skin patches tear, but in 2-3 months, new hair will grow in the transplanted area. After 6 months, all your hair will have grown. At the end of the 12th month the hair transplant development process completes.